Selective Spatial Regularization by Reinforcement Learned Decision Making for Object Tracking
Qing Guo Ruize Han Wei Feng* Zhihao Chen Liang Wan
1College of Intelligence and Computing, Tianjin University
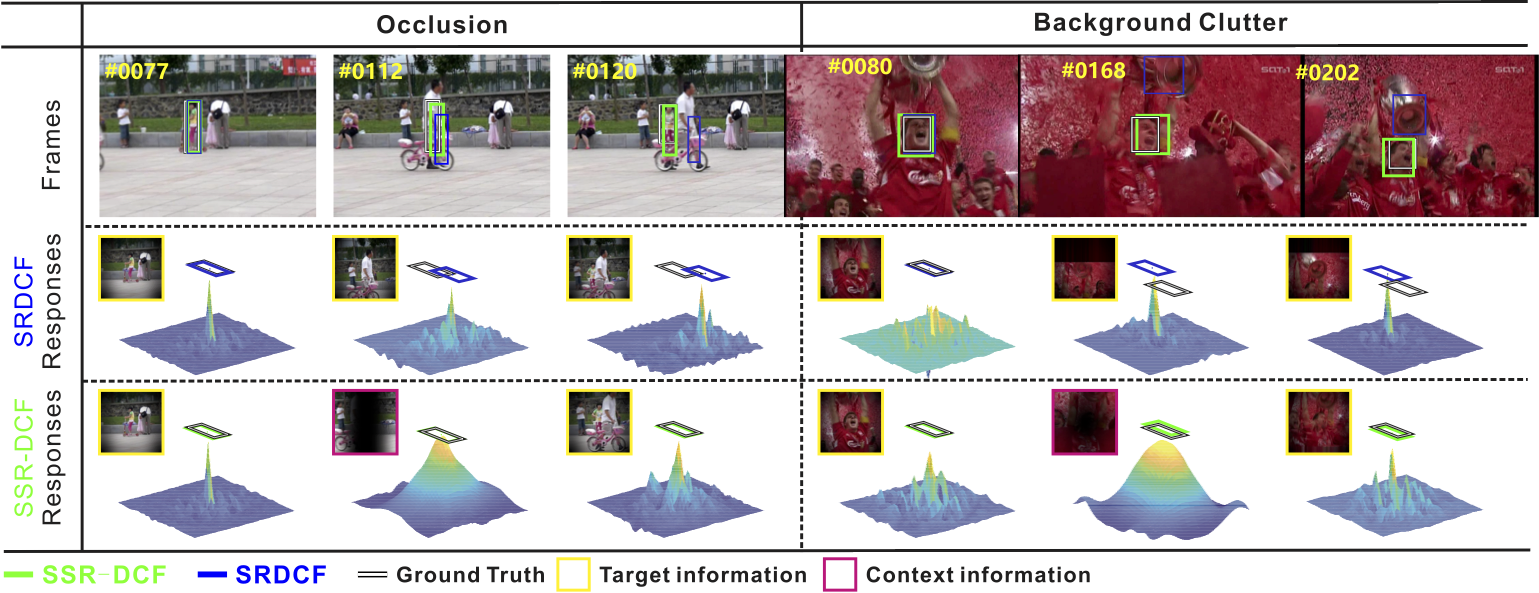
Figure 1. Comparison between SRDCF and the proposed selective spatial regularization based discriminative CF (SSR-DCF) on the cases of occlusion and background clutter. The bounding box results, their response maps, and the information they relied on are shown. When the targets are fully occluded or surrounded by similar objects, e.g., frame #112 in ‘girl2’ and frame #168 in ‘soccer’, SRDCF uses filters that only rely on the target information for localization and produces a false high response at the background, which further leads to erroneous filter updating and encumbers the re-detection of the target at subsequence frames. In contrast, SSR-DCF utilizes the context information when above severe situations happen and gets more discriminative response maps than SRDCF, which further avoids erroneous filter updating and enables to re-detect targets when interferences disappear. Please find intuitive explanations in the text.
Abstract
Spatial regularization (SR) is known as an effective tool to alleviate the boundary effect of correlation filter (CF), a successful visual object tracking scheme, from which a number of state-of-the-art visual object trackers can be stemmed. Nevertheless, SR highly increases the optimization complexity of CF and its target-driven nature makes spatially-regularized CF trackers may easily lose the occluded targets or the targets surrounded by other similar objects. In this paper, we propose selective spatial regularization (SSR) for CF-tracking scheme. It can achieve not only higher accuracy and robustness, but also higher speed compared with spatially-regularized CF trackers. Specifically, rather than simply relying on foreground information, we extend the objective function of CF tracking scheme to learn the target-context-regularized filters using target-contextdriven weight maps. We then formulate the online selection of these weight maps as a decision making problem by a Markov Decision Process (MDP), where the learning of weight map selection is equivalent to policy learning of the MDP that is solved by a reinforcement learning strategy. Moreover, by adding a special state, representing not-updating filters, in the MDP, we can learn when to skip unnecessary or erroneous filter updating, thus accelerating the online tracking. Finally, the proposed SSR is used to equip three popular spatially-regularized CF trackers to significantly boost their tracking accuracy, while achieving much faster online tracking speed. Besides, extensive experiments on five benchmarks validate the effectiveness of SSR.
Introduction
In this paper, we propose selective spatial regularization (SSR) for the CF-tracking scheme, which can obtain higher tracking accuracy and robustness, and meanwhile is much faster during the online process. The major contributions of this work are: 1) We propose an extended objective function for CF tracking scheme to generate target-context-regularized filters by selectively using target-context-driven weight maps tovregularize the learning of correlation filters. 2) We formulate the online selection of different weight maps as a decision making problem via a Markov Decision Process (MDP), where the learning of weight map selection is solved by policy learning of the MDP through a reinforcement learning strategy. Moreover, by adding a special state, representing not-updating filters, in the MDP, we effectively learn when to skip unnecessary or erroneous filter updating, thus to accelerate the online tracking without harming the accuracy. 3) We use the proposed SSR to improve three popular spatially-regularized CF trackers, SRDCF, CCOT and ECO, which validates the feasibility and generality of SSR. Extensive experiments on OTB2013, OTB-2015, VOT-2016, TC-128, and LaSOT verify the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art competitors.
Results on OTB-2013 and 2015
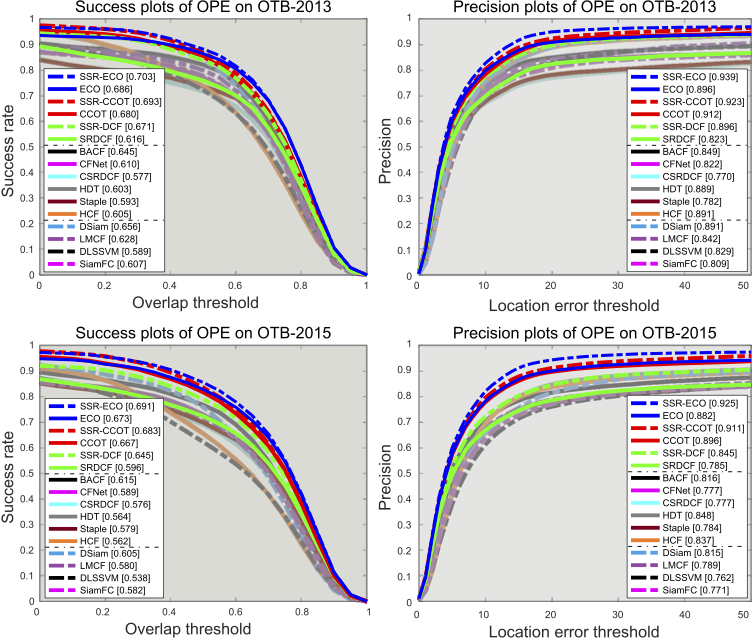
Comparison results on OTB-2013 and OTB-2015. The legend of each tracker shows the AUC score of success plots and precision at 20 pixels of precision plots.
Results on TC128 and LaSOT
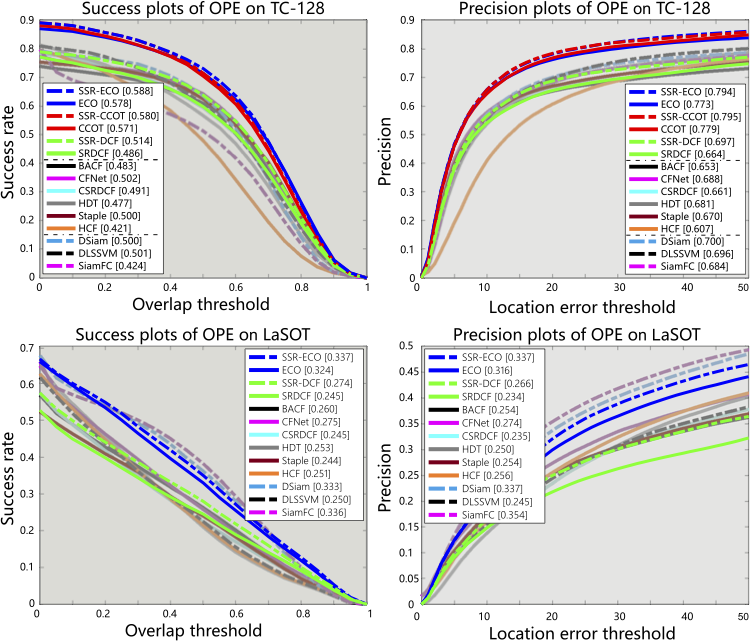
Comparison results on TC128 and LaSOT. The legend of each tracker shows the AUC score of success plots and precision at 20 pixels of precision plots.
Source Code
Source Code (Matlab) and Models: [ Code][ LaSOT results] [ OTB100 results] [ TC128 results]Citation - BibTeX
Qing Guo, Ruize Han, Wei Feng, Zhihao Chen, Liang Wan. Selective Spatial Regularization by Reinforcement Learned Decision Making for Object Tracking.
In IEEE TIP, 2019.(CCF-A).
[ PDF ]
[ BibTeX ]